一、功能说明 二、快速使用 三、实现原理
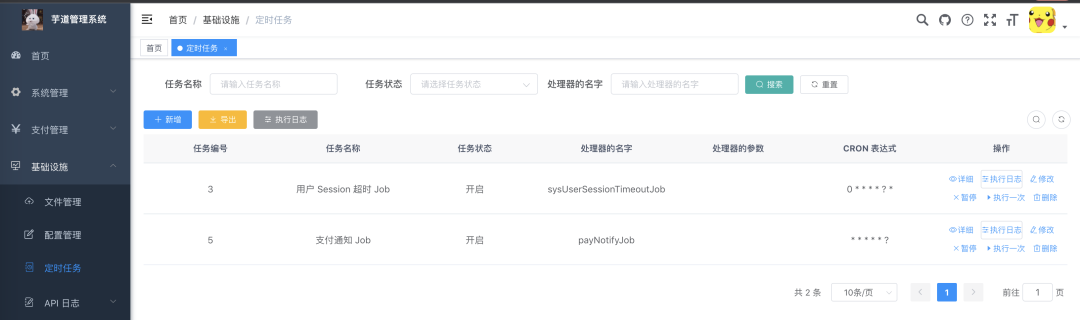
一、功能说明
SpringBoot的定时任务的加强工具,实现对SpringBoot原生的定时任务进行动态管理,完全兼容原生@Scheduled注解,无需对原本的定时任务进行修改
“推荐下自己做的 Spring Boot 的实战项目:
https://github.com/YunaiV/ruoyi-vue-pro
二、快速使用
具体的功能已经封装成SpringBoot-starter即插即用
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.guoyixing</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-super-scheduled</artifactId>
<version>0.3.1</version>
</dependency>
使用方法和源码:
“码云:https://gitee.com/qiaodaimadewangcai/super-scheduled
github:https://github.com/guoyixing/super-scheduled
“推荐下自己做的 Spring Cloud 的实战项目:
https://github.com/YunaiV/onemall
三、实现原理
1、动态管理实现
(1) 配置管理介绍
@Component("superScheduledConfig")
public class SuperScheduledConfig {
/**
* 执行定时任务的线程池
*/
private ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler;
/**
* 定时任务名称与定时任务回调钩子 的关联关系容器
*/
private Map<String, ScheduledFuture> nameToScheduledFuture = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 定时任务名称与定时任务需要执行的逻辑 的关联关系容器
*/
private Map<String, Runnable> nameToRunnable = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 定时任务名称与定时任务的源信息 的关联关系容器
*/
private Map<String, ScheduledSource> nameToScheduledSource = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/* 普通的get/sets省略 */
}
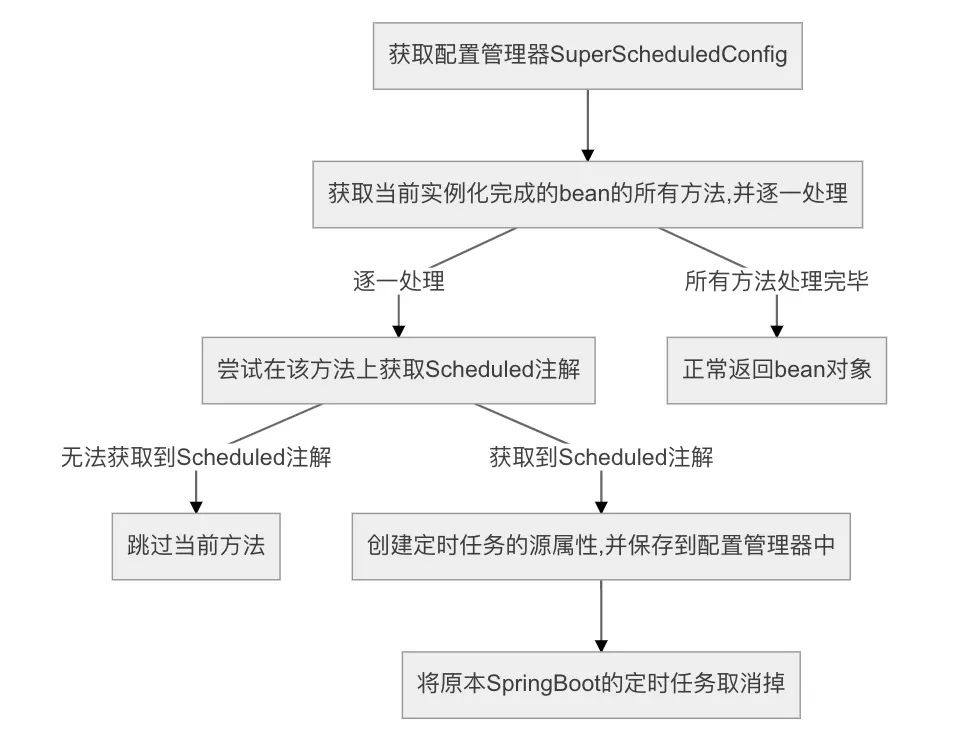
(2) 使用后处理器拦截SpringBoot原本的定时任务
实现ApplicationContextAware接口拿到SpringBoot的上下文 实现BeanPostProcessor接口,将这个类标记为后处理器,后处理器会在每个bean实例化之后执行 使用@DependsOn注解强制依赖SuperScheduledConfig类,让SpringBoot实例化SuperScheduledPostProcessor类之前先实例化SuperScheduledConfig类 -
主要实现逻辑在postProcessAfterInitialization()方法中
@DependsOn({"superScheduledConfig"})
@Component
@Order
public class SuperScheduledPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 实例化bean之前的操作
* @param bean bean实例
* @param beanName bean的Name
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* 实例化bean之后的操作
* @param bean bean实例
* @param beanName bean的Name
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean,
String beanName) throws BeansException {
//1.获取配置管理器
SuperScheduledConfig superScheduledConfig = applicationContext.getBean(SuperScheduledConfig.class);
//2.获取当前实例化完成的bean的所有方法
Method[] methods = bean.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
//循环处理对每个方法逐一处理
if (methods.length > ) {
for (Method method : methods) {
//3.尝试在该方法上获取@Scheduled注解(SpringBoot的定时任务注解)
Scheduled annotation = method.getAnnotation(Scheduled.class);
//如果无法获取到@Scheduled注解,就跳过这个方法
if (annotation == null) {
continue;
}
//4.创建定时任务的源属性
//创建定时任务的源属性(用来记录定时任务的配置,初始化的时候记录的是注解上原本的属性)
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = new ScheduledSource(annotation, method, bean);
//对注解上获取到源属性中的属性进行检测
if (!scheduledSource.check()) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("在" + beanName + "Bean中" + method.getName() + "方法的注解参数错误");
}
//生成定时任务的名称(id),使用beanName+“.”+方法名
String name = beanName + "." + method.getName();
//将以key-value的形式,将源数据存入配置管理器中,key:定时任务的名称 value:源数据
superScheduledConfig.addScheduledSource(name, scheduledSource);
try {
//5.将原本SpringBoot的定时任务取消掉
clearOriginalScheduled(annotation);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("在关闭原始方法" + beanName + method.getName() + "时出现错误");
}
}
}
//后bean保持原有返回
return bean;
}
/**
* 修改注解原先的属性
* @param annotation 注解实例对象
* @throws Exception
*/
private void clearOriginalScheduled(Scheduled annotation) throws Exception {
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "cron", Scheduled.CRON_DISABLED);
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "fixedDelay", -1L);
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "fixedDelayString", "");
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "fixedRate", -1L);
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "fixedRateString", "");
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "initialDelay", -1L);
changeAnnotationValue(annotation, "initialDelayString", "");
}
/**
* 获取SpringBoot的上下文
* @param applicationContext SpringBoot的上下文
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
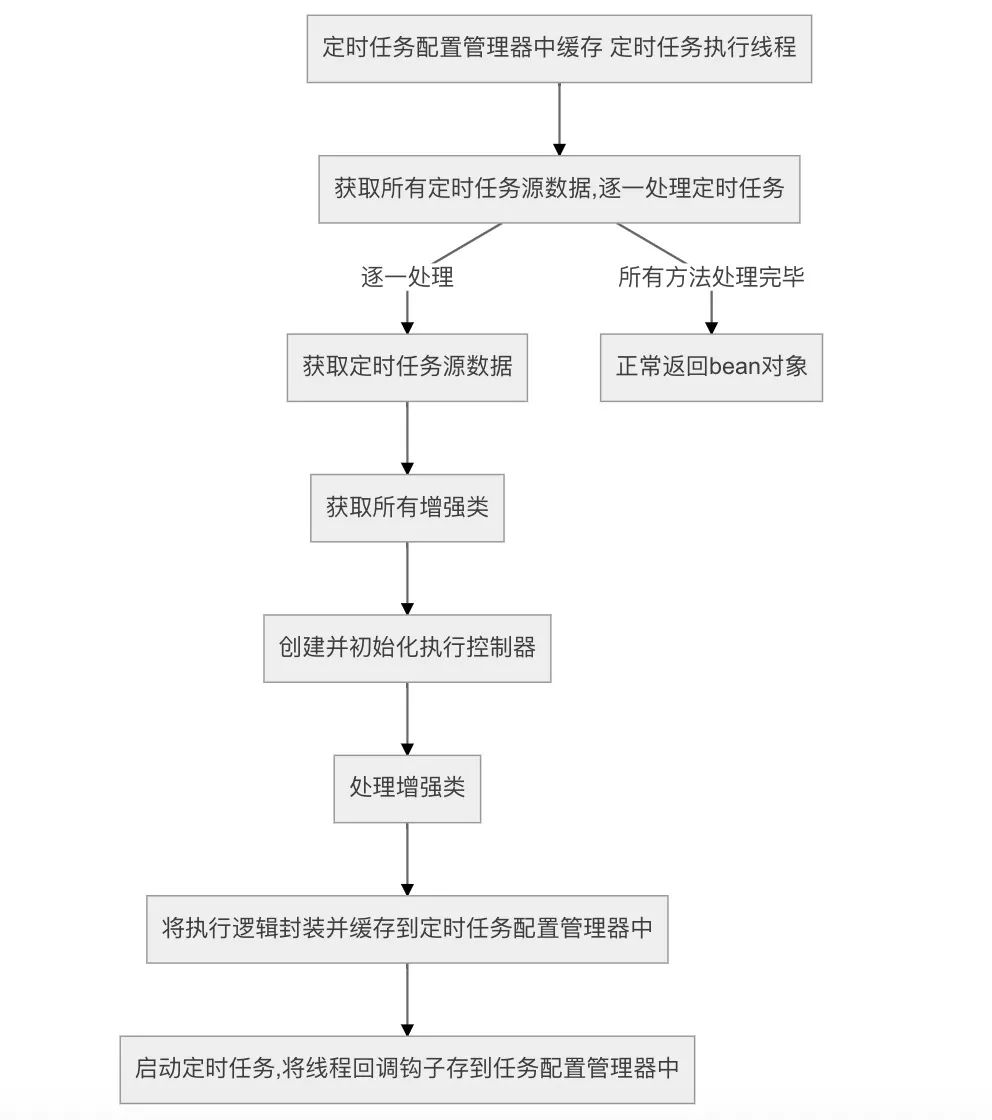
(3) 使用ApplicationRunner初始化自定义的定时任务运行器
实现ApplicationContextAware接口拿到SpringBoot的上下文 使用@DependsOn注解强制依赖threadPoolTaskScheduler类 实现ApplicationRunner接口,在所有bean初始化结束之后,运行自定义逻辑 主要实现逻辑在run()方法中
@DependsOn("threadPoolTaskScheduler")
@Component
public class SuperScheduledApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner, ApplicationContextAware {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private DateTimeFormatter df = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 定时任务配置管理器
*/
@Autowired
private SuperScheduledConfig superScheduledConfig;
/**
* 定时任务执行线程
*/
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolTaskScheduler threadPoolTaskScheduler;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
//1.定时任务配置管理器中缓存 定时任务执行线程
superScheduledConfig.setTaskScheduler(threadPoolTaskScheduler);
//2.获取所有定时任务源数据
Map<String, ScheduledSource> nameToScheduledSource = superScheduledConfig.getNameToScheduledSource();
//逐一处理定时任务
for (String name : nameToScheduledSource.keySet()) {
//3.获取定时任务源数据
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = nameToScheduledSource.get(name);
//4.获取所有增强类
String[] baseStrengthenBeanNames = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(BaseStrengthen.class);
//5.创建执行控制器
SuperScheduledRunnable runnable = new SuperScheduledRunnable();
//配置执行控制器
runnable.setMethod(scheduledSource.getMethod());
runnable.setBean(scheduledSource.getBean());
//6.逐一处理增强类(增强器实现原理后面具体分析)
List<Point> points = new ArrayList<>(baseStrengthenBeanNames.length);
for (String baseStrengthenBeanName : baseStrengthenBeanNames) {
//7.将增强器代理成point
Object baseStrengthenBean = applicationContext.getBean(baseStrengthenBeanName);
//创建代理
Point proxy = ProxyUtils.getInstance(Point.class, new RunnableBaseInterceptor(baseStrengthenBean, runnable));
proxy.setSuperScheduledName(name);
//8.所有的points连成起来
points.add(proxy);
}
//将point形成调用链
runnable.setChain(new Chain(points));
//将执行逻辑封装并缓存到定时任务配置管理器中
superScheduledConfig.addRunnable(name, runnable::invoke);
try {
//8.启动定时任务
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule = ScheduledFutureFactory.create(threadPoolTaskScheduler
, scheduledSource, runnable::invoke);
//将线程回调钩子存到任务配置管理器中
superScheduledConfig.addScheduledFuture(name, schedule);
logger.info(df.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "任务" + name + "已经启动...");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("任务" + name + "启动失败,错误信息:" + e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
}
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
(4) 进行动态管理
@Component
public class SuperScheduledManager {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private DateTimeFormatter df = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
@Autowired
private SuperScheduledConfig superScheduledConfig;
/**
* 修改Scheduled的执行周期
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param cron cron表达式
*/
public void setScheduledCron(String name, String cron) {
//终止原先的任务
cancelScheduled(name);
//创建新的任务
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = superScheduledConfig.getScheduledSource(name);
scheduledSource.clear();
scheduledSource.setCron(cron);
addScheduled(name, scheduledSource);
}
/**
* 修改Scheduled的fixedDelay
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param fixedDelay 上一次执行完毕时间点之后多长时间再执行
*/
public void setScheduledFixedDelay(String name, Long fixedDelay) {
//终止原先的任务
cancelScheduled(name);
//创建新的任务
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = superScheduledConfig.getScheduledSource(name);
scheduledSource.clear();
scheduledSource.setFixedDelay(fixedDelay);
addScheduled(name, scheduledSource);
}
/**
* 修改Scheduled的fixedRate
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param fixedRate 上一次开始执行之后多长时间再执行
*/
public void setScheduledFixedRate(String name, Long fixedRate) {
//终止原先的任务
cancelScheduled(name);
//创建新的任务
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = superScheduledConfig.getScheduledSource(name);
scheduledSource.clear();
scheduledSource.setFixedRate(fixedRate);
addScheduled(name, scheduledSource);
}
/**
* 查询所有启动的Scheduled
*/
public List<String> getRunScheduledName() {
Set<String> names = superScheduledConfig.getNameToScheduledFuture().keySet();
return new ArrayList<>(names);
}
/**
* 查询所有的Scheduled
*/
public List<String> getAllSuperScheduledName() {
Set<String> names = superScheduledConfig.getNameToRunnable().keySet();
return new ArrayList<>(names);
}
/**
* 终止Scheduled
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
*/
public void cancelScheduled(String name) {
ScheduledFuture scheduledFuture = superScheduledConfig.getScheduledFuture(name);
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
superScheduledConfig.removeScheduledFuture(name);
logger.info(df.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "任务" + name + "已经终止...");
}
/**
* 启动Scheduled
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param scheduledSource 定时任务的源信息
*/
public void addScheduled(String name, ScheduledSource scheduledSource) {
if (getRunScheduledName().contains(name)) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("定时任务" + name + "已经被启动过了");
}
if (!scheduledSource.check()) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("定时任务" + name + "源数据内容错误");
}
scheduledSource.refreshType();
Runnable runnable = superScheduledConfig.getRunnable(name);
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = superScheduledConfig.getTaskScheduler();
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule = ScheduledFutureFactory.create(taskScheduler, scheduledSource, runnable);
logger.info(df.format(LocalDateTime.now()) + "任务" + name + "已经启动...");
superScheduledConfig.addScheduledSource(name, scheduledSource);
superScheduledConfig.addScheduledFuture(name, schedule);
}
/**
* 以cron类型启动Scheduled
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param cron cron表达式
*/
public void addCronScheduled(String name, String cron) {
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = new ScheduledSource();
scheduledSource.setCron(cron);
addScheduled(name, scheduledSource);
}
/**
* 以fixedDelay类型启动Scheduled
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param fixedDelay 上一次执行完毕时间点之后多长时间再执行
* @param initialDelay 次执行的延迟时间
*/
public void addFixedDelayScheduled(String name, Long fixedDelay, Long... initialDelay) {
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = new ScheduledSource();
scheduledSource.setFixedDelay(fixedDelay);
if (initialDelay != null && initialDelay.length == 1) {
scheduledSource.setInitialDelay(initialDelay[]);
} else if (initialDelay != null && initialDelay.length > 1) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("次执行的延迟时间只能传入一个参数");
}
addScheduled(name, scheduledSource);
}
/**
* 以fixedRate类型启动Scheduled
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
* @param fixedRate 上一次开始执行之后多长时间再执行
* @param initialDelay 次执行的延迟时间
*/
public void addFixedRateScheduled(String name, Long fixedRate, Long... initialDelay) {
ScheduledSource scheduledSource = new ScheduledSource();
scheduledSource.setFixedRate(fixedRate);
if (initialDelay != null && initialDelay.length == 1) {
scheduledSource.setInitialDelay(initialDelay[]);
} else if (initialDelay != null && initialDelay.length > 1) {
throw new SuperScheduledException("次执行的延迟时间只能传入一个参数");
}
addScheduled(name, scheduledSource);
}
/**
* 手动执行一次任务
*
* @param name scheduled的名称
*/
public void runScheduled(String name) {
Runnable runnable = superScheduledConfig.getRunnable(name);
runnable.run();
}
}
2、增强接口实现
增强器实现的整体思路与SpringAop的思路一致,实现没有Aop复杂
(1) 增强接口
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public interface BaseStrengthen {
/**
* 前置强化方法
*
* @param bean bean实例(或者是被代理的bean)
* @param method 执行的方法对象
* @param args 方法参数
*/
void before(Object bean, Method method, Object[] args);
/**
* 后置强化方法
* 出现异常不会执行
* 如果未出现异常,在afterFinally方法之后执行
*
* @param bean bean实例(或者是被代理的bean)
* @param method 执行的方法对象
* @param args 方法参数
*/
void after(Object bean, Method method, Object[] args);
/**
* 异常强化方法
*
* @param bean bean实例(或者是被代理的bean)
* @param method 执行的方法对象
* @param args 方法参数
*/
void exception(Object bean, Method method, Object[] args);
/**
* Finally强化方法,出现异常也会执行
*
* @param bean bean实例(或者是被代理的bean)
* @param method 执行的方法对象
* @param args 方法参数
*/
void afterFinally(Object bean, Method method, Object[] args);
}
(2) 代理抽象类
public abstract class Point {
/**
* 定时任务名
*/
private String superScheduledName;
/**
* 抽象的执行方法,使用代理实现
* @param runnable 定时任务执行器
*/
public abstract Object invoke(SuperScheduledRunnable runnable);
/* 普通的get/sets省略 */
}
(3) 调用链类
public class Chain {
private List<Point> list;
private int index = -1;
/**
* 索引自增1
*/
public int incIndex() {
return ++index;
}
/**
* 索引还原
*/
public void resetIndex() {
this.index = -1;
}
}
(4) cglib动态代理实现
使用cglib代理增强器,将增强器全部代理成调用链节点Point
public class RunnableBaseInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
/**
* 定时任务执行器
*/
private SuperScheduledRunnable runnable;
/**
* 定时任务增强类
*/
private BaseStrengthen strengthen;
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object result;
//如果执行的是invoke()方法
if ("invoke".equals(method.getName())) {
//前置强化方法
strengthen.before(obj, method, args);
try {
//调用执行器中的invoke()方法
result = runnable.invoke();
} catch (Exception e) {
//异常强化方法
strengthen.exception(obj, method, args);
throw new SuperScheduledException(strengthen.getClass() + "中强化执行时发生错误", e);
} finally {
//Finally强化方法,出现异常也会执行
strengthen.afterFinally(obj, method, args);
}
//后置强化方法
strengthen.after(obj, method, args);
} else {
//直接执行方法
result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
}
return result;
}
public RunnableBaseInterceptor(Object object, SuperScheduledRunnable runnable) {
this.runnable = runnable;
if (BaseStrengthen.class.isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
this.strengthen = (BaseStrengthen) object;
} else {
throw new SuperScheduledException(object.getClass() + "对象不是BaseStrengthen类型");
}
}
public RunnableBaseInterceptor() {
}
}
(5) 定时任务执行器实现
public class SuperScheduledRunnable {
/**
* 原始的方法
*/
private Method method;
/**
* 方法所在的bean
*/
private Object bean;
/**
* 增强器的调用链
*/
private Chain chain;
public Object invoke() {
Object result;
//索引自增1
if (chain.incIndex() == chain.getList().size()) {
//调用链中的增强方法已经全部执行结束
try {
//调用链索引初始化
chain.resetIndex();
//增强器全部执行完毕,执行原本的方法
result = method.invoke(bean);
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new SuperScheduledException(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
} else {
//获取被代理后的方法增强器
Point point = chain.getList().get(chain.getIndex());
//执行增强器代理
//增强器代理中,会回调方法执行器,形成调用链,逐一运行调用链中的增强器
result = point.invoke(this);
}
return result;
}
/* 普通的get/sets省略 */
}
(6) 增强器代理逻辑
com.gyx.superscheduled.core.SuperScheduledApplicationRunner类中的代码片段
//创建执行控制器
SuperScheduledRunnable runnable = new SuperScheduledRunnable();
runnable.setMethod(scheduledSource.getMethod());
runnable.setBean(scheduledSource.getBean());
//用来存放 增强器的代理对象
List<Point> points = new ArrayList<>(baseStrengthenBeanNames.length);
//循环所有的增强器的beanName
for (String baseStrengthenBeanName : baseStrengthenBeanNames) {
//获取增强器的bean对象
Object baseStrengthenBean = applicationContext.getBean(baseStrengthenBeanName);
//将增强器代理成Point节点
Point proxy = ProxyUtils.getInstance(Point.class, new RunnableBaseInterceptor(baseStrengthenBean, runnable));
proxy.setSuperScheduledName(name);
//增强器的代理对象缓存到list中
points.add(proxy);
}
//将增强器代理实例的集合生成调用链
//执行控制器中设置调用链
runnable.setChain(new Chain(points));
来源:blog.csdn.net/qq_34886352/
article/details/106494637
版权申明:内容来源网络,版权归原创者所有。除非无法确认,我们都会标明作者及出处,如有侵权烦请告知,我们会立即删除并表示歉意。谢谢
