什么是跳表
跳表(Skip List)是一种基于有序链表的扩展,是由William Pugh提出的。他在论文《Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees》中详细地介绍了有关跳表结构、插入删除操作的细节。
Skip List 是一种可以用于替代查找树的内存数据结构,其基本原理是在一个有序的链表之上增加一些索引,通过一个随机规则(保证一定概率)来“模拟”二分查找。
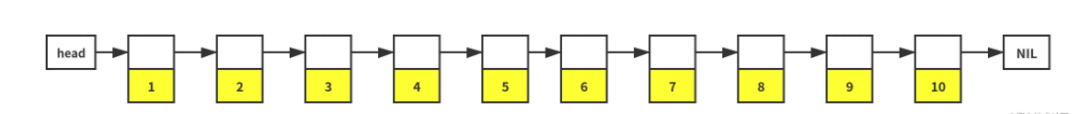
Skip List 的基础是一个有序的链表。但是因为链表在内存中是离散存储的,我们无法在一个有序链表上执行二分查找。
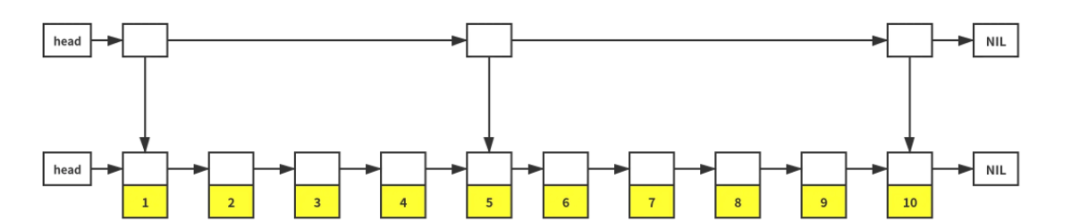
所以,我们决定在这个有序的链表上增加一层索引,用于将这个有序链表一分为二。通过层索引可以将查找量减少一半。
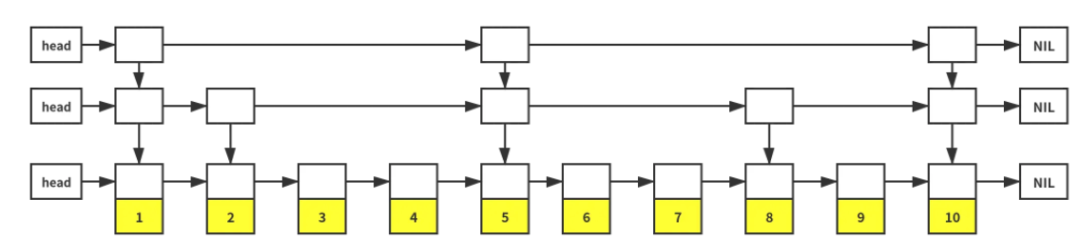
同理,我们可以对左边的链表(1->2->3->4) 建一层索引,将左边一分为二。对右边的链表(6->7->8->9->10)也可以进行一样的操作。如此递归下去……
这样通过付出一些指针的开销,可以将有序链表的查找时间复杂度从 O(n) 降低到和二分查找一样的 O(log2n)。
如果每次都要“精准地一分为二”,插入、删除某个节点的时候会可能会涉及到调整其它节点的指针索引高度。这会让逻辑变得复杂许多,就像红黑树插入、删除节点可能会涉及子树的“旋转”一样。
Skip List 放弃了控制每个节点的索引高度来实现“二分查找”,转而采用一个随机概率规则来确定一个节点的高度。这样,一个节点的插入和删除,只会和它的相邻节点有关,逻辑简单,并且修改范围非常有限(锁粒度可以做到很细),可以实现更高的并发。
跳表优势
数组由于有下标定位,可以采用二分法进行查找,因此读及更新快,但是增加删慢;
链表读写慢(o(n)),但是增删快(o(1));
跳表在链表的基础上,通过索引及空间换时间的思想加快提升读写性能;
平衡树,比如红黑树、AVL 树等,可以保证插入和查找的时间复杂度都是 log2n,但是每次插入可能会涉及到较为复杂的节点旋转等操作导致工程实现复杂。相比平衡树,跳表优势在于,在保证读写性能的同时,大大简化了实现。
跳表的简单实现
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <mutex>
#include <fstream>
std::mutex mtx; // mutex for critical section
std::string delimiter = ":";
//Class template to implement node
template<typename K, typename V>
class Node {
public:
Node() {}
Node(K k, V v, int);
~Node();
K get_key() const;
V get_value() const;
void set_value(V);
// Linear array to hold pointers to next node of different level
Node<K, V> **forward;
int node_level;
private:
K key;
V value;
};
template<typename K, typename V>
Node<K, V>::Node(const K k, const V v, int level) {
this->key = k;
this->value = v;
this->node_level = level;
// level + 1, because array index is from 0 - level
this->forward = new Node<K, V>*[level+1];
// Fill forward array with 0(NULL)
memset(this->forward, , sizeof(Node<K, V>*)*(level+1));
};
template<typename K, typename V>
Node<K, V>::~Node() {
delete []forward;
};
template<typename K, typename V>
K Node<K, V>::get_key() const {
return key;
};
template<typename K, typename V>
V Node<K, V>::get_value() const {
return value;
};
template<typename K, typename V>
void Node<K, V>::set_value(V value) {
this->value=value;
};
// Class template for Skip list
template <typename K, typename V>
class SkipList {
public:
SkipList(int);
~SkipList();
int get_random_level();
Node<K, V>* create_node(K, V, int);
int insert_element(K, V);
void display_list();
bool search_element(K);
void delete_element(K);
int size();
private:
void get_key_value_from_string(const std::string& str, std::string* key, std::string* value);
bool is_valid_string(const std::string& str);
private:
// Maximum level of the skip list
int _max_level;
// current level of skip list
int _skip_list_level;
// pointer to header node
Node<K, V> *_header;
// skiplist current element count
int _element_count;
};
// create new node
template<typename K, typename V>
Node<K, V>* SkipList<K, V>::create_node(const K k, const V v, int level) {
Node<K, V> *n = new Node<K, V>(k, v, level);
return n;
}
// Insert given key and value in skip list
// return 1 means element exists
// return 0 means insert successfully
/*
+------------+
| insert 50 |
+------------+
level 4 +-->1+ 100
|
| insert +----+
level 3 1+-------->10+---------------> | 50 | 70 100
| |
| |
level 2 1 10 30 | 50 | 70 100
| |
| |
level 1 1 4 10 30 | 50 | 70 100
| |
| |
level 0 1 4 9 10 30 40 | 50 | 60 70 100
+----+
*/
template<typename K, typename V>
int SkipList<K, V>::insert_element(const K key, const V value) {
mtx.lock();
Node<K, V> *current = this->_header;
// create update array and initialize it
// update is array which put node that the node->forward[i] should be operated later
Node<K, V> *update[_max_level+1];
memset(update, , sizeof(Node<K, V>*)*(_max_level+1));
// start form highest level of skip list
for(int i = _skip_list_level; i >= ; i--) {
while(current->forward[i] != NULL && current->forward[i]->get_key() < key) {
current = current->forward[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
// reached level 0 and forward pointer to right node, which is desired to insert key.
current = current->forward[];
// if current node have key equal to searched key, we get it
if (current != NULL && current->get_key() == key) {
std::cout << "key: " << key << ", exists" << std::endl;
mtx.unlock();
return 1;
}
// if current is NULL that means we have reached to end of the level
// if current's key is not equal to key that means we have to insert node between update[0] and current node
if (current == NULL || current->get_key() != key ) {
// Generate a random level for node
int random_level = get_random_level();
// If random level is greater thar skip list's current level, initialize update value with pointer to header
if (random_level > _skip_list_level) {
for (int i = _skip_list_level+1; i < random_level+1; i++) {
update[i] = _header;
}
_skip_list_level = random_level;
}
// create new node with random level generated
Node<K, V>* inserted_node = create_node(key, value, random_level);
// insert node
for (int i = ; i <= random_level; i++) {
inserted_node->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = inserted_node;
}
std::cout << "Successfully inserted key:" << key << ", value:" << value << std::endl;
_element_count ++;
}
mtx.unlock();
return ;
}
// Display skip list
template<typename K, typename V>
void SkipList<K, V>::display_list() {
std::cout << "\n*****Skip List*****"<<"\n";
for (int i = ; i <= _skip_list_level; i++) {
Node<K, V> *node = this->_header->forward[i];
std::cout << "Level " << i << ": ";
while (node != NULL) {
std::cout << node->get_key() << ":" << node->get_value() << ";";
node = node->forward[i];
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
// Get current SkipList size
template<typename K, typename V>
int SkipList<K, V>::size() {
return _element_count;
}
template<typename K, typename V>
void SkipList<K, V>::get_key_value_from_string(const std::string& str, std::string* key, std::string* value) {
if(!is_valid_string(str)) {
return;
}
*key = str.substr(, str.find(delimiter));
*value = str.substr(str.find(delimiter)+1, str.length());
}
template<typename K, typename V>
bool SkipList<K, V>::is_valid_string(const std::string& str) {
if (str.empty()) {
return false;
}
if (str.find(delimiter) == std::string::npos) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Delete element from skip list
template<typename K, typename V>
void SkipList<K, V>::delete_element(K key) {
mtx.lock();
Node<K, V> *current = this->_header;
Node<K, V> *update[_max_level+1];
memset(update, , sizeof(Node<K, V>*)*(_max_level+1));
// start from highest level of skip list
for (int i = _skip_list_level; i >= ; i--) {
while (current->forward[i] !=NULL && current->forward[i]->get_key() < key) {
current = current->forward[i];
}
update[i] = current;
}
current = current->forward[];
if (current != NULL && current->get_key() == key) {
// start for lowest level and delete the current node of each level
for (int i = ; i <= _skip_list_level; i++) {
// if at level i, next node is not target node, break the loop.
if (update[i]->forward[i] != current)
break;
update[i]->forward[i] = current->forward[i];
}
// Remove levels which have no elements
while (_skip_list_level > && _header->forward[_skip_list_level] == ) {
_skip_list_level --;
}
std::cout << "Successfully deleted key "<< key << std::endl;
_element_count --;
}
mtx.unlock();
return;
}
// Search for element in skip list
/*
+------------+
| select 60 |
+------------+
level 4 +-->1+ 100
|
|
level 3 1+-------->10+------------------>50+ 70 100
|
|
level 2 1 10 30 50| 70 100
|
|
level 1 1 4 10 30 50| 70 100
|
|
level 0 1 4 9 10 30 40 50+-->60 70 100
*/
template<typename K, typename V>
bool SkipList<K, V>::search_element(K key) {
std::cout << "search_element-----------------" << std::endl;
Node<K, V> *current = _header;
// start from highest level of skip list
for (int i = _skip_list_level; i >= ; i--) {
while (current->forward[i] && current->forward[i]->get_key() < key) {
current = current->forward[i];
}
}
//reached level 0 and advance pointer to right node, which we search
current = current->forward[];
// if current node have key equal to searched key, we get it
if (current and current->get_key() == key) {
std::cout << "Found key: " << key << ", value: " << current->get_value() << std::endl;
return true;
}
std::cout << "Not Found Key:" << key << std::endl;
return false;
}
// construct skip list
template<typename K, typename V>
SkipList<K, V>::SkipList(int max_level) {
this->_max_level = max_level;
this->_skip_list_level = ;
this->_element_count = ;
// create header node and initialize key and value to null
K k;
V v;
this->_header = new Node<K, V>(k, v, _max_level);
};
template<typename K, typename V>
SkipList<K, V>::~SkipList() {
if (_file_writer.is_open()) {
_file_writer.close();
}
if (_file_reader.is_open()) {
_file_reader.close();
}
delete _header;
}
template<typename K, typename V>
int SkipList<K, V>::get_random_level(){
int k = 1;
while (rand() % 2) {
k++;
}
k = (k < _max_level) ? k : _max_level;
return k;
};
读写时间和空间复杂度分析
要实现随机近似二分查找,我们需要保证一个高度为 h 的节点,有 1/2 的概率是高度为 h+1 的节点 :
高度 >= 1 的节点概率为 1。
高度 >= 2 的节点概率为 1/2。
高度 >= 3 的节点概率为 1/4。
…
高度 >= h 的节点概率为 1 / 2^(h-1)。
更通用一点,假设一个高度为 h 的节点,有概率 p 是高度为 h+1 的节点。那么一个长度为 n 的 skip list,需要的指针数量为:N = p^0 * n + p^1 * n + p^2 * n + … = n * (p^0 + p^1 + p^2 + ….) = n(1-p^n) / (1 - p)因为 p < 1,当 n 趋近无穷的时候,p^n 趋近于 0,因此 N = n/(1-p)。Skip List 的空间复杂度是 O(n)*。
如果我们想节省内存空间,可以适当的调低 1/2 这个概率,比如 1/3、1/4,从而减少索引指针个数。
每一层的节点数为n/2^h,n为总节点数,h为具体层数。则当上层总节点数为2的时候,n/2^h = 2 => h = log2n - 1,如果每一层的查找数节点数为x,则查找总复杂度为o(xlog2n),即大致认为是o(log2n)
插入时不需要做额外的节点调整,只需要先找到其需要放的位置,然后修改他和前驱的指向即可。
这样插入节点的时间复杂度为查找的时间复杂度 O(log2n),与修改指针的复杂度 O(1)之和,即也为 O(log2n),删除过程和插入类似,也可以转化为查找和修改指针值,因此复杂度也为 O(log2n)。
LevelDB 的 SkipList 实现
LevelDB 的 SkipList 支持无锁的一写多读,并且只支持查找和插入。LevelDB 通过维护一个写队列来保证同一时刻只有一个线程会写 MemTable。
根据 RandomHeight 的实现,LevelDB 将上面分析的每个元素高度增长的概率设置为 1/4 ,以节省内存。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key, Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == )) {
height++;
}
assert(height > );
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}
FindGreaterOrEqual 查找并返回个大于等于 key 的节点。如果是查找后需要进行插入,需要记录下这个节点的 prev 指针。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key, Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key,
Node** prev) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
if (prev != nullptr) prev[level] = x;
if (level == ) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
}
FindLessThan 查找并返回后一个小于 key 的节点。FindLast 查找并返回后一个节点。Contains 查找 SkipList 是否包含某个 key。
Insert 插入一个 key。前面说了,LevelDB 保证这里同一时刻只会有一个线程在写入,并通过原子地修改指针(SetNext)来保证不影响并发执行的读请求。
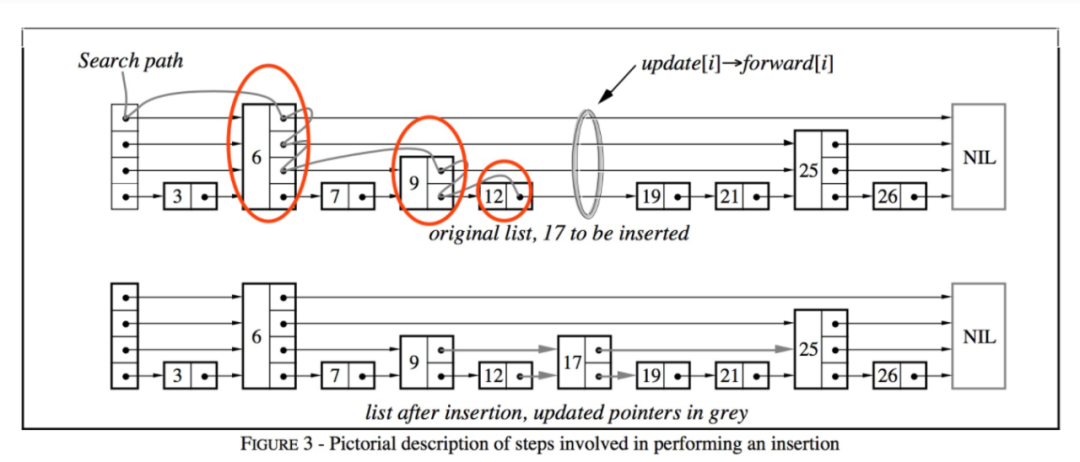
在查找的过程中,不断记录每一层的前任节点,如图中红色圆圈所表示的;
为新插入的节点随机产生层高;在合适的位置插入新节点(例如图中节点12与节点19之间),并依据查找时记录的前任节点信息,在每一层中,以链表插入的方式,将该节点插入到每一层的链接中。
链表插入指:将当前节点的Next值置为前任节点的Next值,将前任节点的Next值替换为当前节点。
template <typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key, Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
// Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == nullptr || !Equal(key, x->key));
int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
// It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (nullptr), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since nullptr sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.store(height, std::memory_order_relaxed);
}
x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = ; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
}
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= );
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].store(x, std::memory_order_release);
}
参考
学会跳表只需要3分钟 | 让你的链表支持二分查找
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1QK4y1Y7mS?from=search&seid=11201728104715062900&spm_id_from=333.337.0.0memory order
https://blog.csdn.net/wzq2009/article/details/106322868不考虑并发的实现
https://github.com/youngyangyang04/Skiplist-CPP/blob/master/skiplist.hLevelDB 完全解析(1):MemTable
https://juejin.cn/post/6844904134223593485LevelDB handbook:
https://leveldb-handbook.readthedocs.io/zh/latest/index.html漫谈 LevelDB 数据结构(一):跳表(Skip List)
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hFaTY8_Kre-bYZ4tbOacqghttps://github.com/youngyangyang04/Skiplist-CPP/blob/master/skiplist.h
来自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VDHwMvLuqWypjnZEXBXJWw
