1. Introduce
过去数十年,学术界对非易失性内存DIMM有大量的研究,但是在这期间,并没有真的DIMM设备,大家都是采用一些emulation techniques,基于对DIMM的特性,仿真出来的;有的通过软件模拟,有的直接通过对DRAM做限速来仿真,等等。随着Intel 3D XPoint技术的成熟,Intel正式发布非易失性内存商业产品Intel’s Optane DC Persistent Memory。不幸的是,现实的DIMM设备和过去模拟的设备似乎在各种性能特性上相差很大(如下图)。基于错误前提,得出来的结论自然也会存在偏差。所以很快有人基于在Intel Optane设备(FAST2020[2]),做了大量的测试,详细分析了基于Intel 3D Xpoint技术的Optane设备在各种场景下的性能特点,并总结了关于Optane的Best Pracitices供大家参考;如果你正准备尝试Optane设备的测试,那么非常推荐你阅读,想必会有所帮助。
(本文主要是简单罗列FAST2020 An Empirical Guide to the Behavior and Use of Scalable Persistent Memory[2]一些数据和结论,感兴趣的可以直接去预印网站上下载:https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03583?context=cs.PF)
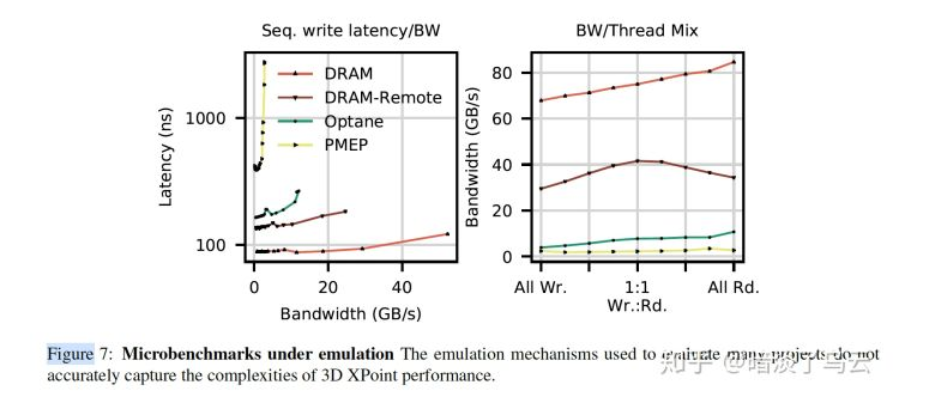
(如上图,DRAM、DRAM-Remote、PMEP为三种常见的DIMM设备emulation techniques)
2. 3D Xpoint Memory
2.1. 3D Xpoint DIMM
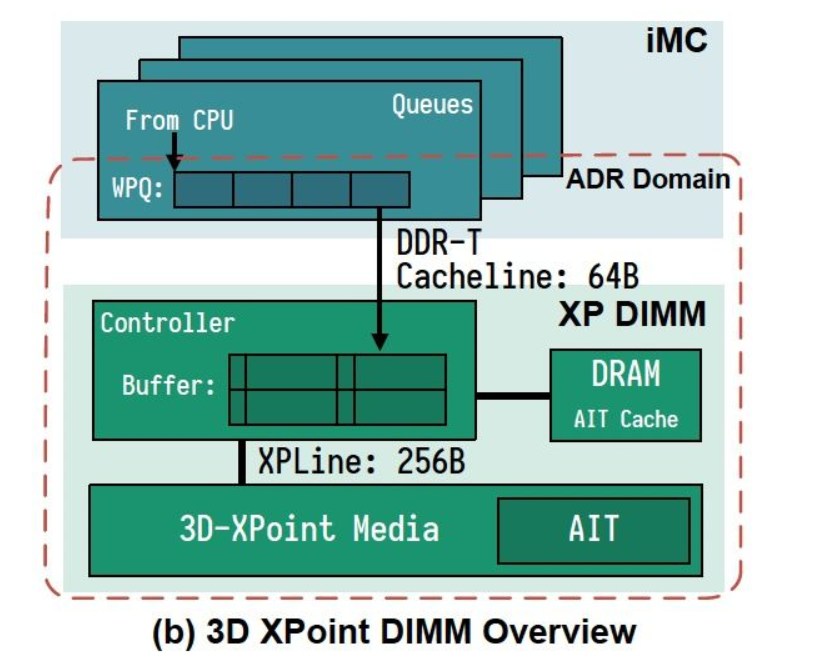
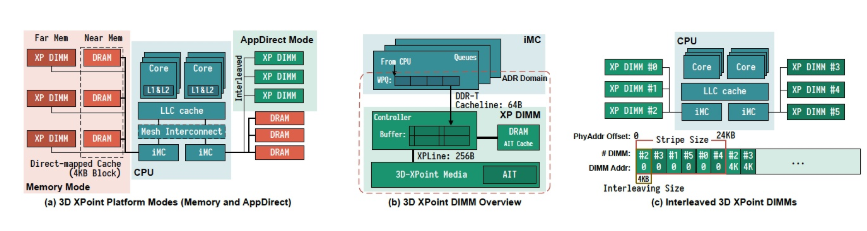
如上图,3D Xpoint DIMM Overview,外部通过XP Controller访问DIMM设备,XP Controller主要负责逻辑地址到地物理介质映射的工作。其中一个比较重要的特点就是3D Xpoint物理介质的小访问单元是256B,也就是上图中XPLine,所有XP Controller对于小的request,将采用read-modify-write来实现,所以会存在一定的放大。所以这里不难看出,3D Xpoint DIMM设备的byte-address能力是有一定性能牺牲的。
2.2. Operation Modes & Pragramming
3D Xpoint提供了两种模式:
- Memory:直接充当main memory,不提供持久性,在CPU会将其直接当main memory使用。
- APP Direct:提供持久性,CPU会将其看做一中单独的持久性内存设备
Pragramming[1]:
intel cpu给程序提供了多种控制store order的指令,分别是:
- cflush(Cache Line Flush)
- 能将Cache line刷到main memory中
- cflushopt(Optimized CLFLUSH)
- 对cflush的优化,可以实现并发的对不同的Cache Line做flush
- clwb( cache line write back)
- 它和cflushopt类似,只会将Cache Line flush到main memory之后,Cache Line中的仍会保存
- ntstore( non-temporal store)
- 绕过缓存,直接写入main memory
一般还需要结合sfence(store屏障)来保证写入main memory的顺序。
3. Performance Characterization
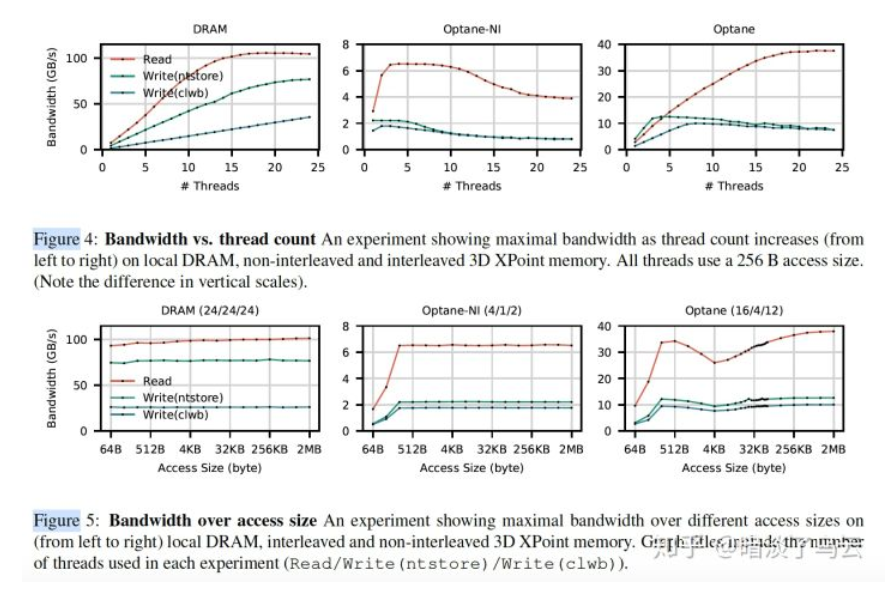
3D Xpoint的性能数据,大家可以简单看看
- bw vs DRAM
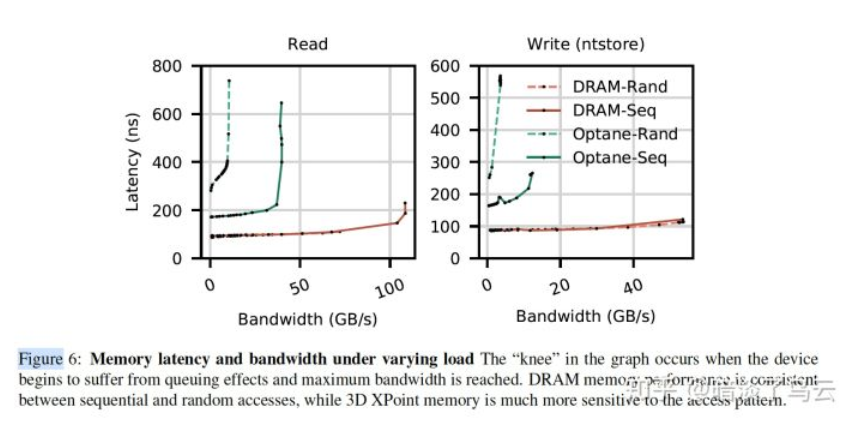
- latency under load
4. Best Practices
重点来了,3D Xpoint有哪些经验性的佳时间呢?
- (1)Avoid random accesses smaller than < 256 B
在2.1.小节介绍过3D Xpoint的小物理介质更新单元是256B,所以,对于较小的request,将会采用read-modify-write技术来更新,会存在一定的放大,那么大量的小request,自然会影响整个3D Xpoint的有效带宽,更多的不同场景测试数据可以参见原文。
- (2)Use non-temporal stores when possible for large transfers, and control of cache evictions.
所谓的non-temporal store,就是上文中提到的ntstore指令。首先看如下图,不难发现ntstore在大写的情况下,带宽明显有优势,且没有损失latency。
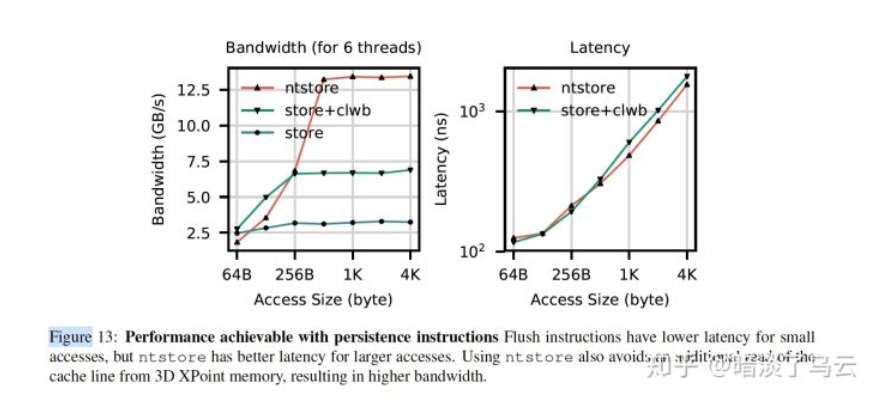
此外,sfence对ststore指令的影响小,如下图。

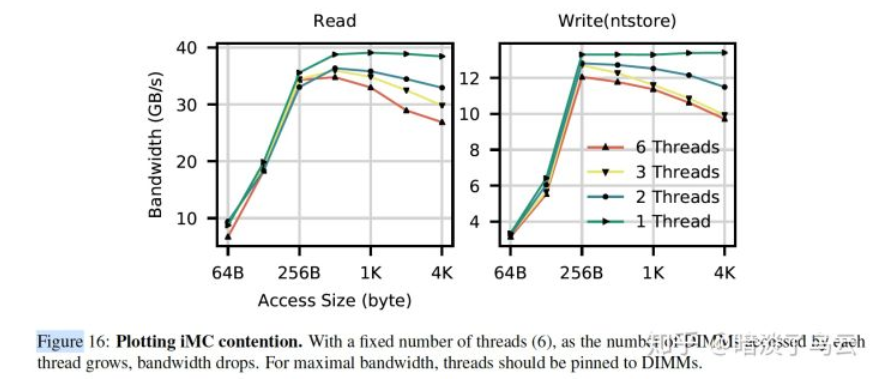
- (3)Limit the number of concurrent threads accessing a 3D XPoint DIMM.
需要尽量控制对单个DIMM设备的并发访问,因为可能会造成两个方面的竞争:
- Contention in the XPBuffer
如下图,在对hotspot region访问的时候,会出现长尾。

- Contention in the iMC(integrate memory controller)
如下图展示了随着线程的变多,bw反而有下降的趋势。
- (4)Avoid mixed or multi-threaded accesses to remote NUMA nodes
相比DRAM,3D Xpoint跨NUMA节点访问性能下降非常明显:
For writes, remote 3D XPoint memory’s latency is 2.53 (ntstore) and 1.68 higher compared to local. For bandwidth, remote 3D XPoint can achieve 59.2% and 61.7% of local read and write bandwidth at optimal thread count
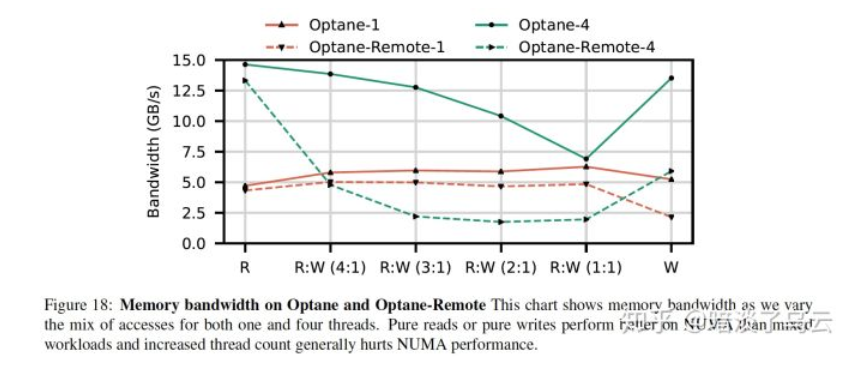
如上图,显示了不同rw-mixed情况下,访问local和remote node的bw差异。
Notes
限于作者水平,难免在理解和描述上有疏漏或者错误的地方,欢迎共同交流;部分参考已经在正文和参考文献列表中注明,但仍有可能有疏漏的地方,有任何侵权或者不明确的地方,欢迎指出,必定及时更正或者删除;文章供于学习交流,转载注明出处
参见文献
[1]. Persistent Memory Programming. "https://www.usenix.org/system/files/login/articles/login_summer17_07_rudoff.pdf"
[2]. Yang, Jian, et al. "An Empirical Guide to the Behavior and Use of Scalable Persistent Memory." arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.03583 (2019).