生产端 Confirm 消息确认机制
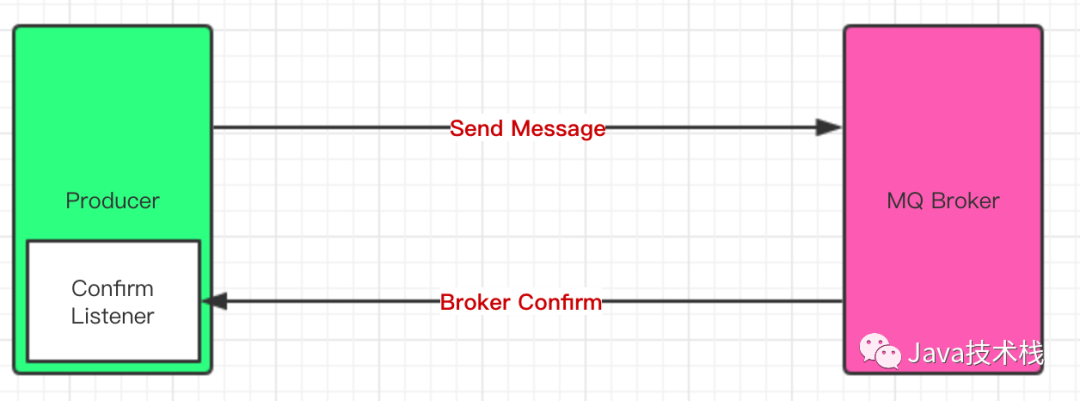
消息的确认,是指生产者投递消息后,如果 Broker 收到消息,则会给我们生产者一个应答。
生产者进行接收应答,用来确定这条消息是否正常的发送到 Broker ,这种方式也是消息的可靠性投递的核心保障!
Confirm 确认机制流程图
如何实现Confirm确认消息?
步:在 channel 上开启确认模式:
channel.confirmSelect()第二步:在 channel 上添加监听:
channel.addConfirmListener(ConfirmListener listener);, 监听成功和失败的返回结果,根据具体的结果对消息进行重新发送、或记录日志等后续处理!
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConfirmListener;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConfirmProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
String exchangeName = "test_confirm_exchange";
String routingKey = "item.update";
//指定消息的投递模式:confirm 确认模式
channel.confirmSelect();
//发送
final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 5 ; i++) {
String msg = "this is confirm msg ";
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey, null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
}
//添加一个确认监听, 这里就不关闭连接了,为了能保证能收到监听消息
channel.addConfirmListener(new ConfirmListener() {
/**
* 返回成功的回调函数
*/
public void handleAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
System.out.println("succuss ack");
System.out.println(multiple);
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
/**
* 返回失败的回调函数
*/
public void handleNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
System.out.printf("defeat ack");
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
}
});
}
}
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ConfirmConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
String exchangeName = "test_confirm_exchange";
String queueName = "test_confirm_queue";
String routingKey = "item.#";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, "topic", true, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//一般不用代码绑定,在管理界面手动绑定
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//创建消费者并接收消息
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
}
};
//设置 Channel 消费者绑定队列
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
}
}
我们此处只关注生产端输出消息
Send message : this is confirm msg
Send message : this is confirm msg
Send message : this is confirm msg
Send message : this is confirm msg
Send message : this is confirm msg
succuss acktrue耗时:3ms
succuss acktrue耗时:4ms
注意事项
我们采用的是异步 confirm 模式:提供一个回调方法,服务端 confirm 了一条或者多条消息后 Client 端会回调这个方法。除此之外还有单条同步 confirm 模式、批量同步 confirm 模式,由于现实场景中很少使用我们在此不做介绍,如有兴趣直接参考官方文档。关注公众号Java技术栈可以获取更多系列RabbitMQ教程。
我们运行生产端会发现每次运行结果都不一样,会有多种情况出现,因为 Broker 会进行优化,有时会批量一次性 confirm ,有时会分开几条 confirm。
succuss ack true
耗时:3ms
succuss ack false
耗时:4ms
或者
succuss ack true
耗时:3ms
Return 消息机制
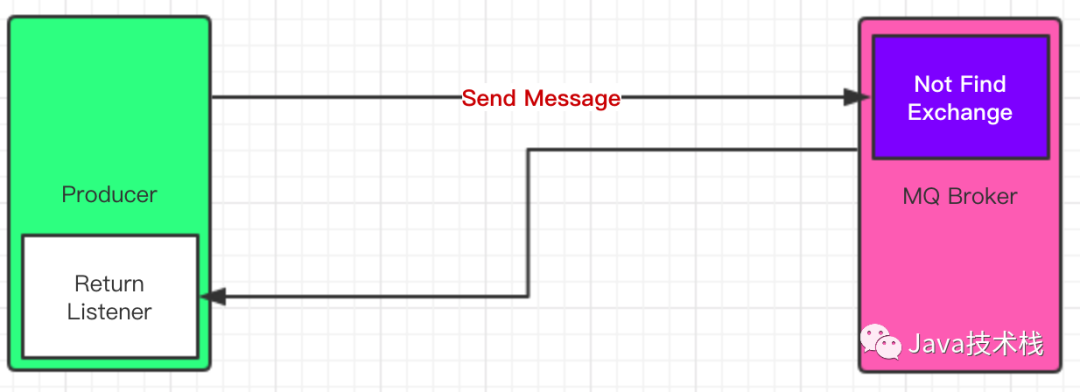
Return Listener 用于处理一-些不可路由的消息!
消息生产者,通过指定一个
Exchange和Routingkey,把消息送达到某一个队列中去,然后我们的消费者监听队列,进行消费处理操作!但是在某些情况下,如果我们在发送消息的时候,当前的 exchange 不存在或者指定的路由 key 路由不到,这个时候如果我们需要监听这种不可达的消息,就要使用
Return Listener !在基础API中有一个关键的配置项:
Mandatory:如果为true,则监听器会接收到路由不可达的消息,然后进行后续处理,如果为false,那么 broker 端自动删除该消息!
Return 消息机制流程图
Return 消息示例
首先我们需要发送三条消息,并且故意将第 0 条消息的
routing Key设置为错误的,让他无法正常路由到消费端。mandatory设置为true路由不可达的消息会被监听到,不会被自动删除.即channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, errRoutingKey, true,null, msg.getBytes());后添加监听即可监听到不可路由到消费端的消息
channel.addReturnListener(ReturnListener r))
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReturnListeningProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
String exchangeName = "test_return_exchange";
String routingKey = "item.update";
String errRoutingKey = "error.update";
//指定消息的投递模式:confirm 确认模式
channel.confirmSelect();
//发送
for (int i = ; i < 3 ; i++) {
String msg = "this is return——listening msg ";
//@param mandatory 设置为 true 路由不可达的消息会被监听到,不会被自动删除
if (i == ) {
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, errRoutingKey, true,null, msg.getBytes());
} else {
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey, true, null, msg.getBytes());
}
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
}
//添加一个确认监听, 这里就不关闭连接了,为了能保证能收到监听消息
channel.addConfirmListener(new ConfirmListener() {
/**
* 返回成功的回调函数
*/
public void handleAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
System.out.println("succuss ack");
}
/**
* 返回失败的回调函数
*/
public void handleNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
System.out.printf("defeat ack");
}
});
//添加一个 return 监听
channel.addReturnListener(new ReturnListener() {
public void handleReturn(int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("return relyCode: " + replyCode);
System.out.println("return replyText: " + replyText);
System.out.println("return exchange: " + exchange);
System.out.println("return routingKey: " + routingKey);
System.out.println("return properties: " + properties);
System.out.println("return body: " + new String(body));
}
});
}
}
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReturnListeningConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. 创建一个 ConnectionFactory 并进行设置
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
//2. 通过连接工厂来创建连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//3. 通过 Connection 来创建 Channel
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//4. 声明
String exchangeName = "test_return_exchange";
String queueName = "test_return_queue";
String routingKey = "item.#";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, "topic", true, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//一般不用代码绑定,在管理界面手动绑定
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
//5. 创建消费者并接收消息
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
}
};
//6. 设置 Channel 消费者绑定队列
channel.basicConsume(queueName, true, consumer);
}
}
我们只关注生产端结果,消费端只收到两条消息。
Send message : this is return——listening msg
Send message : this is return——listening msg
Send message : this is return——listening msg
return relyCode: 312
return replyText: NO_ROUTE
return exchange: test_return_exchange
return routingKey: error.update
return properties: #contentHeader<basic>(content-type=null, content-encoding=null, headers=null, delivery-mode=null, priority=null, correlation-id=null, reply-to=null, expiration=null, message-id=null, timestamp=null, type=null, user-id=null, app-id=null, cluster-id=null)
return body: this is return——listening msg
succuss ack
succuss ack
succuss ack
消费端 Ack 和 Nack 机制
消费端进行消费的时候,如果由于业务异常我们可以进行日志的记录,然后进行补偿!如果由于服务器宕机等严重问题,那我们就需要手工进行ACK保障消费端消费成功!消费端重回队列是为了对没有处理成功的消息,把消息重新会递给Broker!一般我们在实际应用中,都会关闭重回队列,也就是设置为False。
参考 api
void basicNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple, boolean requeue) throws IOException;`
void basicAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException;
如何设置手动 Ack 、Nack 以及重回队列
首先我们发送五条消息,将每条消息对应的循环下标 i 放入消息的
properties中作为标记,以便于我们在后面的回调方法中识别。其次, 我们将消费端的 ·
channel.basicConsume(queueName, false, consumer);中的autoAck属性设置为false,如果设置为true的话 将会正常输出五条消息。我们通过
Thread.sleep(2000)来延时一秒,用以看清结果。我们获取到properties中的num之后,通过channel.basicNack(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false, true);将num为0的消息设置为 nack,即消费失败,并且将requeue属性设置为true,即消费失败的消息重回队列末端。
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AckAndNackProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
String exchangeName = "test_ack_exchange";
String routingKey = "item.update";
String msg = "this is ack msg";
for (int i = ; i < 5; i++) {
Map<String, Object> headers = new HashMap<String, Object>();
headers.put("num" ,i);
AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.deliveryMode(2)
.headers(headers)
.build();
String tem = msg + ":" + i;
channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, routingKey, true, properties, tem.getBytes());
System.out.println("Send message : " + msg);
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AckAndNackConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");
factory.setVirtualHost("/");
factory.setUsername("guest");
factory.setPassword("guest");
factory.setAutomaticRecoveryEnabled(true);
factory.setNetworkRecoveryInterval(3000);
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
String exchangeName = "test_ack_exchange";
String queueName = "test_ack_queue";
String routingKey = "item.#";
channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, "topic", true, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(queueName, false, false, false, null);
//一般不用代码绑定,在管理界面手动绑定
channel.queueBind(queueName, exchangeName, routingKey);
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if ((Integer) properties.getHeaders().get("num") == 0) {
channel.basicNack(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
} else {
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
};
//6. 设置 Channel 消费者绑定队列
channel.basicConsume(queueName, false, consumer);
}
}
我们此处只关心消费端输出,可以看到第 0 条消费失败重新回到队列尾部消费。
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:1'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:2'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:3'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:4'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:0'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:0'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:0'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:0'
[x] Received 'this is ack msg:0'