一,引言
接着上一篇使用 EF Core 操作 Azure CosmosDB 生成种子数据,今天我们完成通过 EF Core 实现CRUD一系列功能。EF Core 3.0 提供了CosmosDB 数据库提供程序的个可用的版本,今天我们使用 EF Core 3.1在尝试使用Cosmos DB 来存储和构建 Asp.NET Core 应用程序时,可能还有一些差异。
1,CosmosDB 不会生成的主键,Cosmos DB不会像SQL数据库那样创建主键。如果需要添加到 Cosmos DB中,则可能会使用类似GUID 字符串的名称。
2,Cosmos DB 不支持EF Core 迁移
--------------------我是分割线--------------------
二,正文
1,Repository 基类仓储实现类
将之前创建好的UserContext 注入基类仓储中
注意,在更新操作中,有个小坑
每个项目都必须具有 id 给定分区键的值。默认情况下,EF Core通过使用“ |”将区分符和主键值连接起来来生成该值。作为分隔符。仅当实体进入 Added 状态时才生成键值。如果实体 id 在.NET类型上没有属性来存储值,则在附加实体时可能会出现问题。
将实体标记为首先添加,然后将其更改为所需状态,我这里将状态改为 “Modified”
public virtual bool Update(TEntity entity) { Db.Add(entity); Db.Entry(entity).State = EntityState.Modified; return true; }
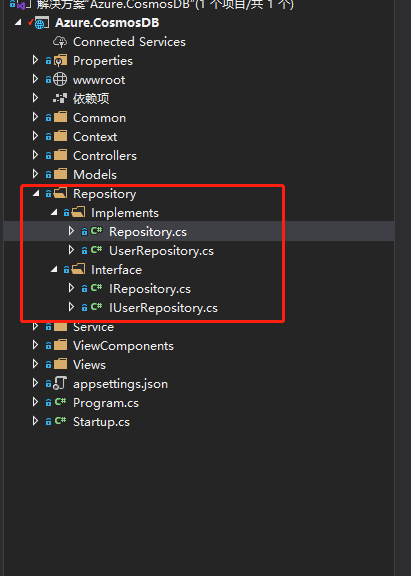
以下是整个仓储层的结构
2,实现业务层 Service 方法
2.1,这里我们的业务层的模型视图为 “UserViewModel”,但是我们的仓储使用的是实体数据模型 "UserModel",这里我引用 Automapper,进行对象转化 。
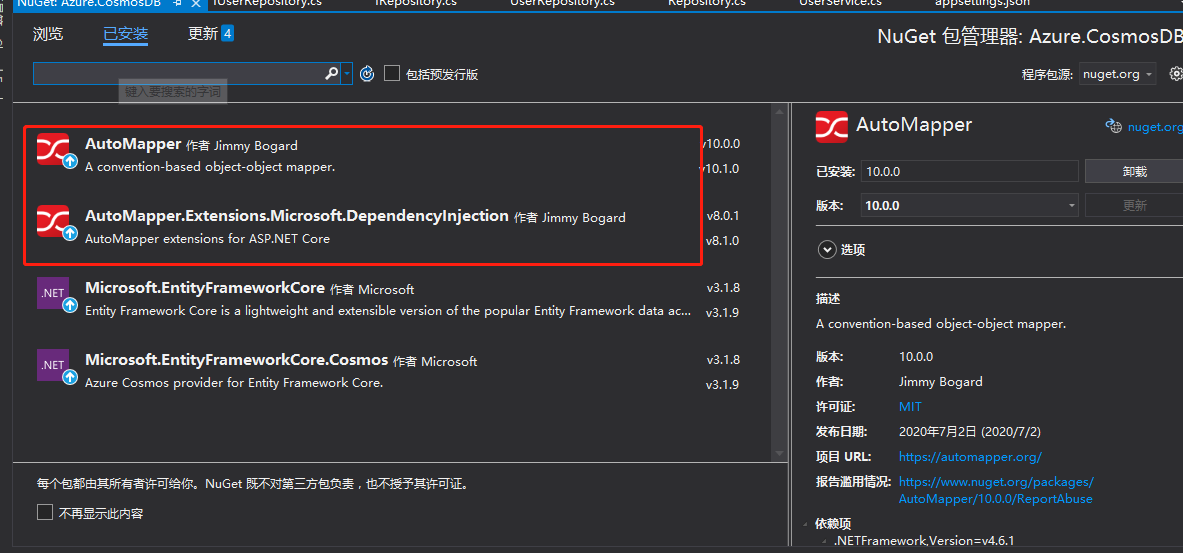
使用程序包管理控制台进行安装
1 | Install-Package AutoMapper -Version 10.0.0 |
1 | Install-Package AutoMapper.Extensions.Microsoft.DependencyInjection -Version 8.0.1 |
2.2,配置构建函数,用来创建关系映射
public DomainToViewModelMappingProfile() { CreateMap<UserModel, UserViewModel>(); }
public ViewModelToDomainMappingProfile() { //手动进行配置 CreateMap<UserViewModel, UserModel>(); }
全局 AutoMapper 配置文件
/// <summary> /// 静态全局 AutoMapper 配置文件 /// </summary> public class AutoMapperConfig { public static MapperConfiguration RegisterMappings() { //创建AutoMapperConfiguration, 提供静态方法Configure,一次加载所有层中Profile定义 //MapperConfiguration实例可以静态存储在一个静态字段中,也可以存储在一个依赖注入容器中。 一旦创建,不能更改/修改。 return new MapperConfiguration(cfg => { //这个是领域模型 -> 视图模型的映射,是 读命令 cfg.AddProfile(new DomainToViewModelMappingProfile()); //这里是视图模型 -> 领域模式的映射,是 写 命令 cfg.AddProfile(new ViewModelToDomainMappingProfile()); }); } }
2.3,创建UserService 实现类,IApplicationService、IUserService 接口
3,创建 UserController 的CRUD 方法及页面
3.1,用户列表,用户详情控制器方法
// GET: User public ActionResult Index() { return View(_userService.GetAll()); } // GET: User/Details/5 public ActionResult Details(string partitionKey) { try { // TODO: Add insert logic here // 执行查询方法 var userViewModel= _userService.GetById(partitionKey); return View(userViewModel); } catch { return View(); } }
3.2 用户列表,用户信息详细页面
Index.cshtml(用户列表)
@model IEnumerable<Azure.CosmosDB.Models.UserViewModel> @{ ViewData["Title"] = "Index"; } <h1>Index</h1> <p> <a asp-action="Create">Create New</a> </p> <table class="table"> <thead> <tr> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Id) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Age) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Address) </th> <th></th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Id) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Age) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Address) </td> <td> @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { partitionKey = item.PartitionKey }) | @Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { partitionKey = item.PartitionKey }) | @Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { partitionKey = item.PartitionKey }) </td> </tr> } </tbody> </table>
Details.cshtml(用户详情)
@model Azure.CosmosDB.Models.UserViewModel @{ ViewData["Title"] = "Details"; Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml"; } <h1>Details</h1> <div> <h4>UserViewModel</h4> <hr /> <dl class="row"> <dt class = "col-sm-2"> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.PartitionKey) </dt> <dd class = "col-sm-10"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.PartitionKey) </dd> <dt class = "col-sm-2"> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Id) </dt> <dd class = "col-sm-10"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Id) </dd> <dt class = "col-sm-2"> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name) </dt> <dd class = "col-sm-10"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Name) </dd> <dt class = "col-sm-2"> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Age) </dt> <dd class = "col-sm-10"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Age) </dd> <dt class = "col-sm-2"> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Address) </dt> <dd class = "col-sm-10"> @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Address) </dd> </dl> </div> <div> @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { partitionKey = Model.PartitionKey }) | <a asp-action="Index">Back to List</a> </div>
4,依赖注入仓储,服务模型以及AutoMap 配置等
// 注入 应用层Application services.AddScoped<IUserService, UserService>(); // 注入 基础设施层 - 数据层 services.AddScoped<IUserRepository, UserRepository>(); //添加服务 services.AddAutoMapper(typeof(AutoMapperConfig)); //启动配置 AutoMapperConfig.RegisterMappings();
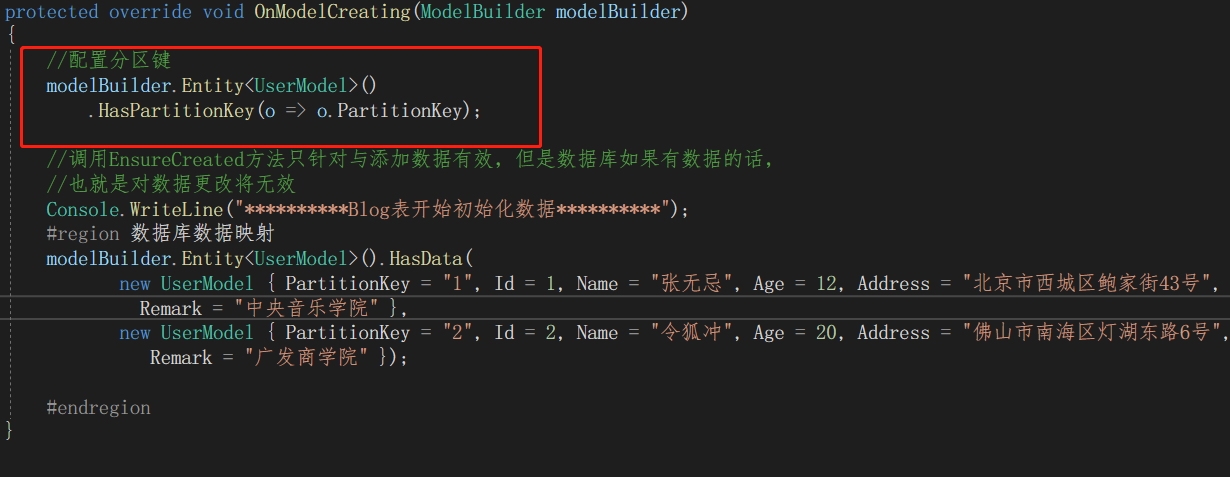
5,配置分区键(分区键属性可以是任何类型,只要将其转换为string)
默认情况下,EF Core将在创建分区时将分区键设置为的容器 "_partitionkey" 而不为其提供任何值。但是要充分利用 Azure Cosmos 的性能,应使用经过精心选择的分区键。可以通过调用HasPartitionKey进行配置:
//配置分区键 modelBuilder.Entity<UserModel>() .HasPartitionKey(o => o.PartitionKey);
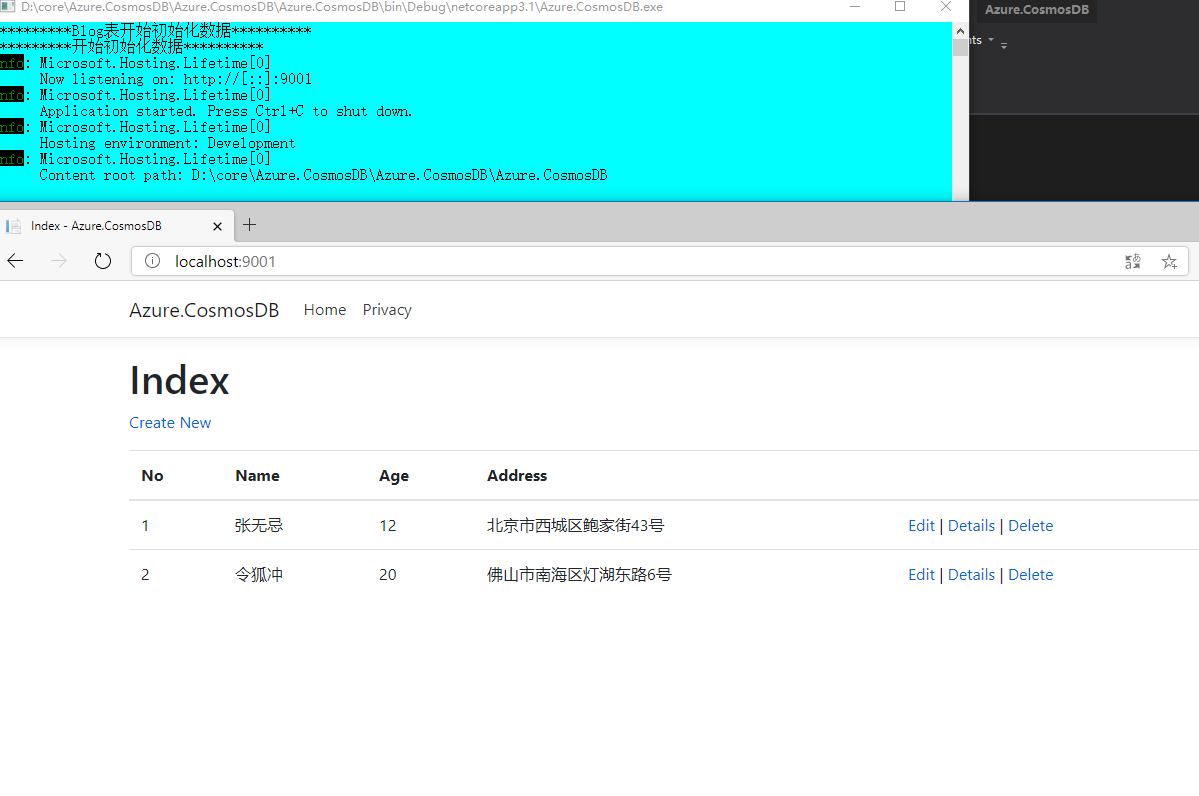
运行项目,可以看到用户列表信息,同时点击数据的 “Details” 可以看到用户数据详情信息。
ok,这里就不再演示运行后,测试各个增删改查的方法,大家可以下载代码,配置本地环境,运行代码进行测试
撒花🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉,今天的分析到此结束。
三,结尾
写这篇文章,花了我比预期更长的时间,主要耗时用在写Demo 上,查文档,写测试等。希望对大家有用。当然也可以加深我们对Cosmos DB可以做什么以及EF Core 3.1 如何操作 Cosmos DB 数据库所提供程序的有进一步的了解。
如果没有大家没有条件在Azure 上创建Cosmos DB 进行测试,学习,可以使用 “Azure Cosmos DB 仿真器”,仿真器在本地运行,并使用localdb存储结果。它还带有一个不错的界面,用于查看/编辑数据。
github:https://github.com/yunqian44/Azure.CosmosDB.git
作者:Allen
版权:转载请在文章明显位置注明作者及出处。如发现错误,欢迎批评指正。
